Power
Overview
This function obtains the result of a number raised to a power.
CHelper.Math.Pow(Base, Power)
The parameters of this function can be defined as Xpaths, variables, or numbers.
Considerations
- Input parameters must be double.
- The supported attribute types to use as input XPath parameter (or Xpaths stored in variables) are: integer, currency, float, real.
- The function returns an error if the Base is between 1 and -1 and the Power is either too long or a negative number.
- The function returns an error if the Base is either too long and the Power is greater than zero.
- The function returns an error if the Base is negative and the Power is not an integer.
- The function returns an error if the Base is not between 1 and -1 and Power is too long.
- The function returns an error if the Base is zero and the Power is negative.
- The function returns an error if the Base or Power are undefined.
- Use the IsNaN function to validate the parameters used are numbers.
Example
In a Credit Request Process, a customer wishes to know what would be the total amount that he/she has to pay in a Personal loan after six months under a given interest rate.
This amount can be calculated using the following formula:
Where Po is the requested amount, i is the monthly interest rate, and P is the amount at month n.
To perform this calculation in Bizagi, you can use the Power function. This function receives two parameters: Number and power.
As the requested amount and interest rate are known, the final amount can be easily calculated as follows:
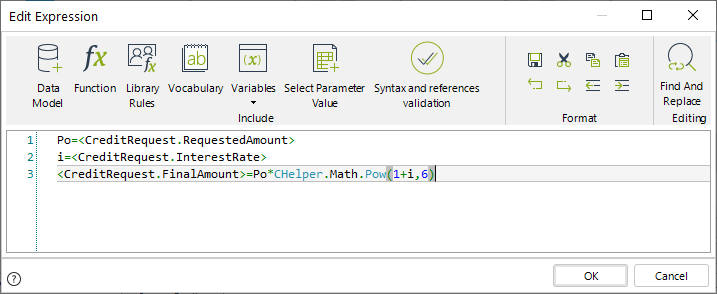
//Obtain the parameters of the formula in variables
Po=<CreditRequest.RequestedAmount>
i=<CreditRequest.InterestRate>
//Apply the formula to obtain the final amount
<CreditRequest.FinalAmount>=Po*CHelper.Math.Pow(1+i,6)